Table of Contents
Introduction
Air compressor safety is an ongoing commitment. Review and improve your safety protocols continuously to stay ahead of potential hazards. Whether you’re a seasoned operator or new to air compressor safety precautions, prioritizing these safety practices ensures a secure and productive work environment.
One of today’s most valuable technologies works on the premise that compressing a volume of air into a smaller area significantly raises its pressure.
Air compressors generate high-pressure air that can be used to power various tools, including impact wrenches and paint guns. When handled properly, pressurized air is incredibly safe and strong.
Making sure that the operator has received the necessary air compressor safety training(can be animated safety videos) and is familiar with the specific model being used is essential to guarantee the safe operation of air compressors.
Reading the instruction booklet and operating the device according to the recommended procedures is crucial. In this article, we’ll discuss a few of the top recommendations for air compressor safety precautions and compressed air safety toolbox talk topics.
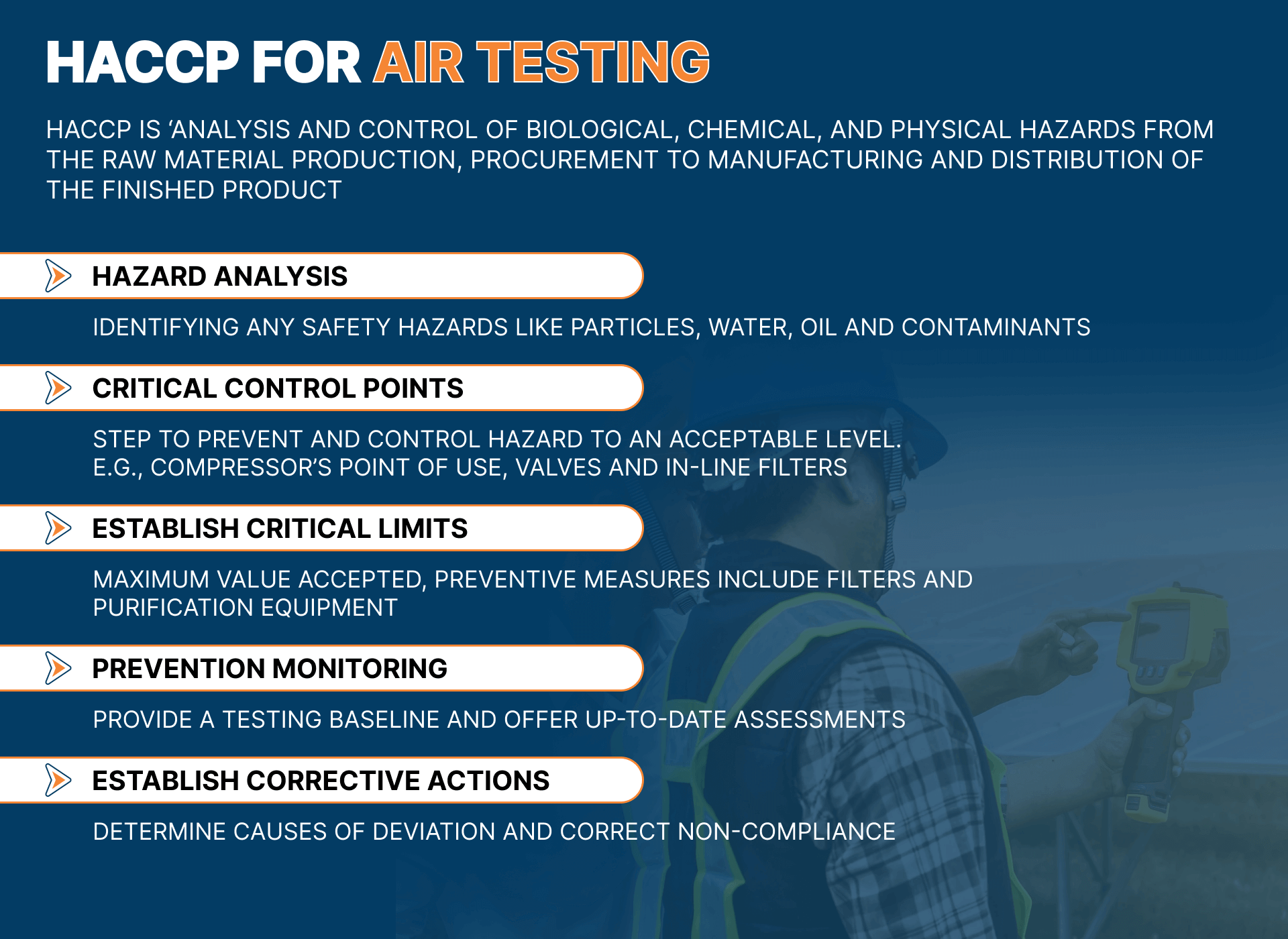
Air Compressor Hazards And Control Measures
Pre-Task Planning
Check the compressor before using it. Check to see if it is in good working order and that the lubrication is appropriate. Please check the oil level if necessary. If you need to add oil, do not overfill it or let any leak onto the compressor.
Ensure that the compressor receives fresh air and the air filter is clean. Replace the filter if it appears to be unclean. Air compressor safety demands that all moving parts are protected so that employees won’t unintentionally come into contact with them.
Air compressor accidents can occur if the compressor is not grounded correctly. This is especially important in areas where flammable or explosive gases may be present. In addition, static electricity from certain compressed air tools can pose a severe hazard.
Compressor exhaust should always be directed away from air intakes and windows, and gasoline—or diesel-powered compressors should not be used indoors.
When using an electric compressor, make sure the power outlet is grounded. Improper grounding is a common cause of air compressor accidents. If using an extension cable, ensure it is no longer than the manual recommends.
On most gasoline or diesel engine-driven compressors, you’ll open the start valve before starting the engine. After it has started, close the tank drain valve and the start valve. Never tighten the drain valve using tools. Let the engine cool if more gasoline needs to be added.
Examine Your Evaluations And Pressure
A system consists of an air compressor, the tools it drives, and the pipelines, hoses, and fittings that link them all together. Confirming that every system component can satisfactorily meet your needs is critical.
Ensure that all system components are rated to handle the air compressor safety requirements. Air compressor hazards and control measures must be understood to prevent over-pressurization. Even better, the ratings should exceed the compressor’s maximum pressure for additional safety.
The shutdown values for the air supply should be placed close to the area of work so that, in an emergency, the airflow may be stopped right away.
Any air receiver tank should have the proper pressure gauges and safety valves, which should be set below the tank’s maximum pressure.
The hoses and pipes that transport air ought to be clean, debris-free, and in good working order. If at all possible, the hoses should be suspended from above the work area to lessen the chance that someone may trip over them or that they will kink up while being used.
Before removing a tool without a fast disconnect fitting, turn off the air supply at the control value and let the tool release any remaining pressure. When you’re done using the compressor, turn off the motor (and disconnect it if it’s powered by electricity). Close the regulator valve and let out any remaining pressurized air.
Open the drain valve and keep it open until the compressor is used again to prevent condensation-related damage.
Using Compressors With Common Sense
Most air compressor accidents occur due to misuse or a lack of personal protective equipment (PPE). Air compressor hazards and control measures include never aiming the air stream or an impact tool toward a coworker. Cleaning oneself with compressed air is equally dangerous and strictly prohibited.
Moreover, the presence of experienced personnel for system maintenance and inspection is vital. While this may not prevent all air compressor accidents, it significantly reduces risks caused by mechanical issues.
Most importantly, make sure that all components of your systems that use compressed air are cleaned, maintained, and subject to routine inspections by experienced staff.
While these measures may not completely prevent air compressor safety hazards, they will lessen those brought on by mechanical issues.
We’ve put up a list of typical safety considerations to help with your routine maintenance program and keep your compressor in prime shape.
Air Compressor Safeties
Conclusion
Releasing safety pressure in air compressors is a vital practice that cannot be overlooked. Understanding and applying proper air compressor safety precautions prevents incidents, protects workers, and ensures compliance with workplace regulations. Ensuring the safe and efficient use of air compressors involves more than just routine maintenance; it requires a keen understanding of the risks associated with high-pressure systems and the steps needed to mitigate them.
Safety measures in handling air compressor pressure release not only protect the equipment but, more importantly, safeguard the health and lives of your team. A proactive approach to pressure management will help avoid costly downtime, injuries, and potential fatalities.
Stay informed, stay vigilant, and always prioritize safety when dealing with air compressors.



