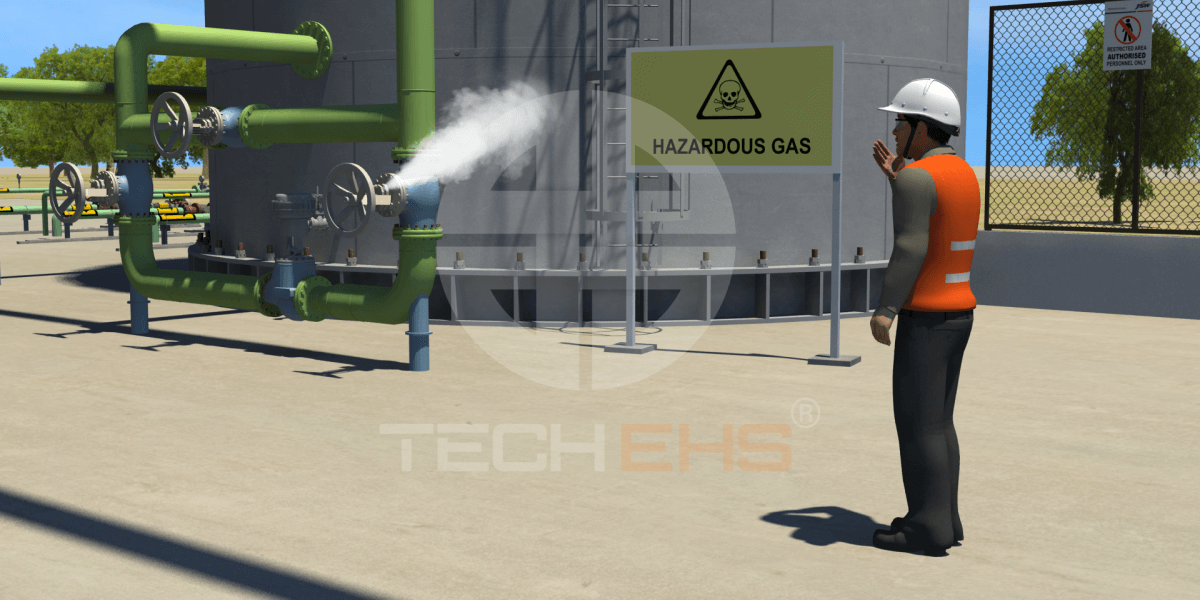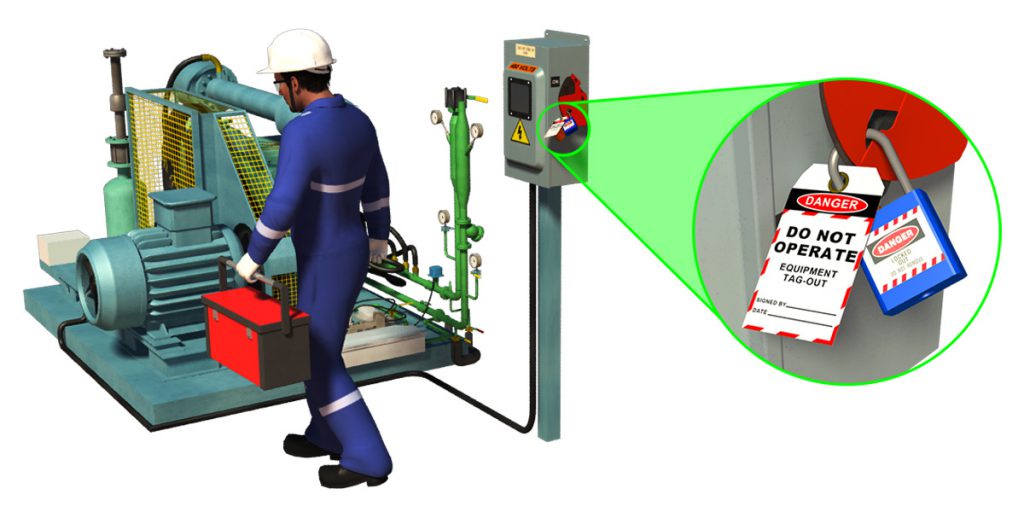
In less than 10 days, a worker’s hand got crushed and two of them got injured as they suffered from the partial amputation of their fingers as workers were operating machines without adequate safety guards and procedures in place.
This incident takes us back to the year 2016 wherein a company suffered severe penalties. Reasons, the company:
Rewinding the scenario
Had the following been in place, the accident would have been avoided.
Talk about machines, and they are like a double-edged sword.
On one hand, they build a level of efficiency that is tough to reach for manual operations. This means production increases along with your bottom line.
On the other hand, they are extremely dangerous, especially since there is often the need for an operator or some human involvement. These accidents can range from a crushed finger to amputation and death (given in the example above). So how are these risks reduced?
The answer is safeguarding by way of implementing machine guard safety.
The basic rule is that any machine part, function, or process that may cause injury must be safeguarded.
As machines continue to become high-tech and complicated, we should keep up with the new advances in Industry 4.0 and strive our best to protect ourselves.
Underlining the essential machine guarding requirements
One must make sure that staff and employees are familiar with machine safety rules and hold regular training sessions to update and reinforce them.
The Primary is to understand and identify when and where safeguards are needed and how they coincide with the operations, whether be a fixed guard, interlocking guard, or any other safety device.
Ask these questions:

Top 10 Golden safety rules
One of the motivations to have the idea of golden rules or 10 rules, originally comes from rule simplification. The reason is, any safety professional’s first response would be ‘oh, my company’s got too many rules’ – so, we boil it down to just those ones that are essential and get rid of all the complexity.
Following machine safety rules serve (3) purposes –
Guidelines for action.
They’re things that you draw on.
They tell you how to do things.
The software’s near-miss analysis can be utilized to provide significant insights for further strategic decisions.
1. Ensure Safe Operations: Machine Guarding and Properly Installed Safeguards
There are rules and regulations that govern machine safety, and the important query remains the installation of proper machine guarding safeguards. As far as machine operators are concerned, it’s the responsibility of a business owner to follow these regulations and ensure that all employees who work on or around machines do so in complete safety.
Machine operators should have the ability to recognize the required machine guarding safeguards and should be perfectly aware when problems surround them. Training programs should emphasize that the legally required machine guarding safeguards are correctly installed and adjusted before the equipment is operated.
2. Never remove machine safeguards or try to get around them
Normally, it’s tempting for a machine operator to remove a safeguard that’s annoying, or the team attempts to bypass if the guard is an obstruction in getting on the job. Even though whatever the reason, this is, undoubtedly, one of the most dangerous things to do around machinery. For the simple reason being, safeguards are present for a reason and should not be removed at any cost.
3. Never Use a Machine with Unauthorized or Damaged Machine Guarding Safeguards
There are chances that unauthorized machine guarding safeguards are installed in such a way that they don’t comply with the existing regulations.
Machinery shouldn’t be operated in such circumstances, or where the properly authorized machine guarding safeguards remain in a damaged condition.
4. In case of a machine safeguard problem, immediately report it to your supervisor
Machine operators should immediately report damage or safeguard failures, whose prime responsibility remains to resolve the safety issues. Only when all the problems are resolved may the operation of the machinery be resumed.
5. Lubricate machine parts without removing the safeguard
Many machines are accessed for lubrication purposes without removing safeguards, via oil reservoirs that might be located outside the guard. If access is not possible with the safeguards still on, the machine must first be switched off and locked out, before one removes the guards.
6. Remove machine safeguards after lock-out/tag-out
If safeguards are removed for any reason, such as maintenance or replacement, it must be done after lock-out, tag-out, or isolation of the equipment. It applies also to all machine maintenance, whether scheduled or reactive.
7. Avoid creating new safety hazards, e.g. new pinch points, or object falling into a machine’s moving parts
Hazardous pinch points are mostly found around various types of roller and gear assemblies, couplings, flywheels, spindles, and drive drums. Junctions, their terminals, and convex curves on conveyor belts show nip hazards, and their locations near skirt plates, feed hoppers, and tracking.
Any object, if it is intentionally or accidentally dropped into a machine can create a new pinch point. Damages to the equipment, along with the operator, are possible.
8. Always wear PPE – don’t let jewelry, loose clothing, or long hair dangle anywhere near machines
A pinch point may is any point where the whole or part of a person’s body is at risk of being caught in machinery.
This doesn’t only mean a machine’s own moving parts, but also between its moving and its stationary parts, and again any part of the machine and other materials.
These include falling objects or materials attached to the machine operators themselves.
Loose clothing, long hair, or dangling jewelry also, constitute a nip hazard. These items can be caught up in the machine’s moving parts and cause additional safety hazards. Employees should wear the required PPE in the workplace, such as masks, gloves, glasses, aprons, boots, and hats.
Integrating PPE software into your safety protocols not only enhances compliance with machine guarding regulations but also provides a proactive approach to maintaining a safe working environment.
9. Never walk away from a machine until all the parts have stopped moving
It’s important to explain and make clear to an employee during training that a machine is not necessarily at rest just because it’s been switched off. Some parts continue to move, such as fans, cooling elements, rollers, gears, and rotating parts, and may constitute hazardous pinch points.
No machine should be left unattended even if there is any part moving.
10. Ask questions or concerns about machine safety or working with safeguards to your supervisor
Operators who are in any doubt, or who have questions regarding the safe operations, must always refer these concerns to their supervisor immediately. They should not attempt to deal with the issue themselves.
These top ten machine safety rules are designed for protecting your employees while working around machinery.
Machine safety is a wide-ranging and important topic, however, and embraces many aspects such as health and safety at work and prevailing standards.