Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Potential Hazards in Boiler Operation
- Risk Audit and Compliance Audit
- Importance of Boiler Safety
- Boiler Safety Operation and Procedures
- Routine Maintenance and Inspections
- Emergency Preparedness
- Technological Solutions
- Role of Animation In Boiler Safety
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions(FAQ)
Introduction
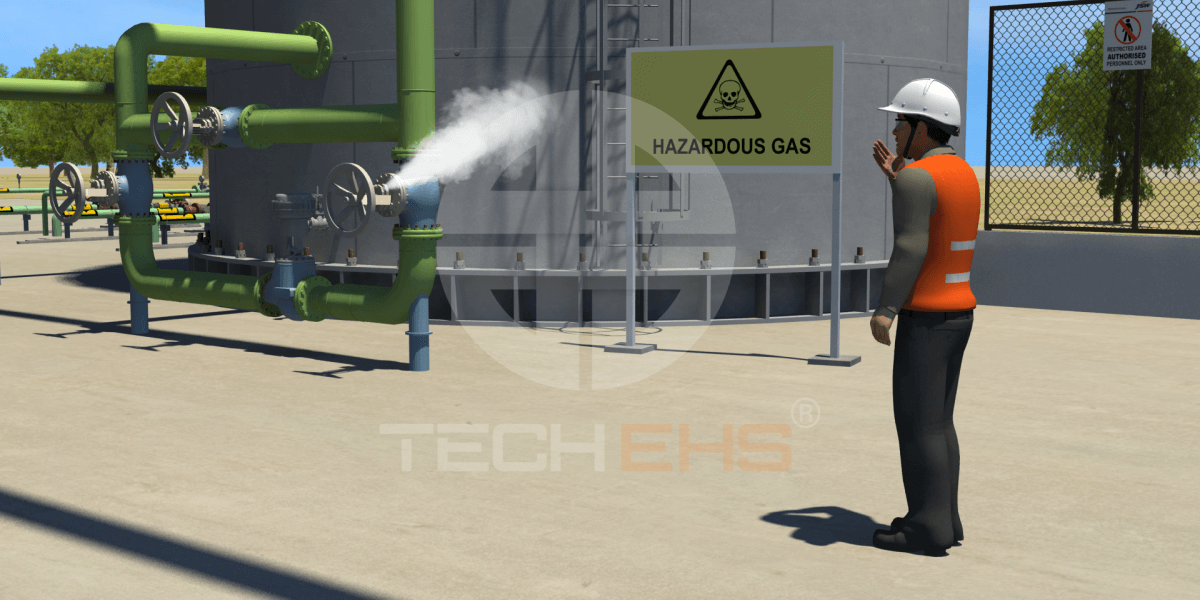
Boilers burn fuel in large quantities, attain high temperature and pressure zones, handle high-energy steam in bulk, transmit it through pipelines, and finally use steam for various utilities. These activities pose a significant threat to human safety, property, and asset protection because of steam’s gigantic destruction power once it finds leakage/release when the container or pipeline gives way.
The invention of steam power by James Watt, a British Scientist, was a landmark in the power generation field since it enabled human civilization to harness the energy content of various fuels.
Boilers, fuelled by common resources like wood and predominantly coal, have been instrumental in various traction purposes such as driving trains and rolling road surfaces. The abundance of coal globally ensures that boiler operation will continue to be a significant industrial installation for the foreseeable future. Thus, there stand a significant importance of boilers in industries.
Potential Hazards in Boiler Operation
EHS audit management is crucial for organizations’ safety and for evaluating internal and external compliances.
A complaint audit evaluates the appropriate working conditions of people, policies, equipment, and other technical procedures. A risk compliance audit ensures that all three are effectively compliant in their fields.
Audit risk management ensures that operational risks are identified and measured appropriately. Risk-based auditing involves sufficient identification, control, monitoring, and governance, which enables safety officers to efficiently identify loopholes, deficiencies, and grey areas in the system.
For example, a chemical factory must adhere to the ever-changing regulations regarding chemicals and their handling. They need proper audit management for regulatory compliance, hazard communications, inventory management, and environmental protocols. Therefore, risk auditing will ensure that all the above compliances are met according to industry standards and client requirements. Additionally, it will make your organization ready for compliance audits—surprise or planned!
Risk Audit and Compliance Audit
Boilers burn fuel in large quantities, attain high temperature and pressure zones, handle high-energy steam in bulk, transmit it through pipelines, and finally use steam for various utilities. These activities pose a significant threat to human safety, property, and asset protection because of steam’s gigantic destruction power once it finds leakage/release when the container or pipeline gives way.
There are potential hazards in boiler operations;
Importance of Boiler Safety
Safety operating procedures that is, SOP, awareness, and proper training, play a significant role as many accidents have been reported due to exploding boilers, wrongly installed boilers, inadequately designed boilers, and those that were not correctly operated.
Due to the severe nature of the operation of boiler & its accessories, every country of the world has framed a stringent and compact regulation on the safe use of Boiler operation – including The Boiler Act & Rules under the charge of enforcing authorities such as Boiler Inspectorate or Directorate of Boiler Operation, e.g., to ensure the reliability of welding joints in boiler tubes and pipelines, a particular category of High-Pressure Welders, holding a special category of ‘Licentiate’ has been made compulsory for boiler industries.
Using a particular boiler grade of seamless steel pipes is an essential technical requirement. Integrated Boiler combine comprises bulk transportation, handling, storage, crushing, powdering, firing into the boiler, super-heated steam generation/storage/utilities, and associated high temperature/pressure/energy zone. All these units are full of hazards/risks with enormous harming potential.
Boiler Safety Operation and Procedures
To ensure that the boiler operations are safe and sound, here are some essential boiler safety tips to follow;
Routine Maintenance and Inspections
Always ensure that the boiler is in its best state. This not only prolongs the equipment’s life but also ensures that risks are taken care of proactively. If noticed initially, any malfunctioning can be treated well before it becomes a hazard.
Maintenance and inspections must be documented daily, weekly, and monthly. EHS software can help maintain a proper checklist for inspection purposes.
Emergency Preparedness
Every employee must know the emergency shutdown procedures. Also, fire safety and evacuation plans must be in place and updated regularly to avoid casualties if hazards happen.
Technological Solutions
Technology advancements must be incorporated for boiler safety. Automated monitoring systems, safety valves and pressure relief mechanisms must be in sync with the safety data and raise alarms or send notifications if trouble is detected.
Safety is not just a requirement, but a hallmark of every individual operation, from the smallest sub-assembly to the entire thermal power complex. It permeates every aspect of the process, from standard operating procedures to technological upkeep, maintenance discipline, and even temporary closure and decommissioning. Each phase demands specific and expert technical inputs to ensure the safety of the working group, people nearby, and the assets in and around the boiler installation.
Role of Animation In Boiler Safety
Considering the impending hazards and threats in boiler operation, the standard operating procedure (SOP), which takes care of safety, production, productivity, and quality aspects, needs special care and expertise for framing and introduction.
Safety operating procedures can be best explained via animation, which can act as a tool to demonstrate the best practices. Animation videos can visually show the hazards in boiler operation and emphasize on steam boiler safety.
If you want to know more, you certainly must contact TECH EHS animation experts. The technical expert ensure that the videos portray real-life situations in the most understanding way. Also, the videos are curated in native languages so that the employees understand them in the way they need to be explained.
Once you employ animation to train the employees, you will see a noticeable difference in the training and understanding ways!
Conclusion
Ensuring safety in boiler operation is not merely a regulatory requirement but a crucial commitment to protecting lives, preserving equipment, and maintaining operational efficiency. By understanding the potential hazards and implementing stringent safety protocols, we can significantly reduce the risk of accidents and enhance the overall reliability of boiler systems.
Regular maintenance and inspections, coupled with proper training and the use of advanced monitoring technologies, form the backbone of a robust safety strategy. Compliance with industry standards and legal requirements further reinforces this safety net, providing a structured framework within which boilers can operate securely and efficiently.
Remember, there are potential consequences of neglect and the positive outcomes that arise from a proactive approach to safety.
Ultimately, the goal is to foster a culture of safety that permeates every aspect of boiler operation. By prioritizing safety, we not only protect our personnel and assets but also ensure the long-term success and sustainability of our operations.